Bitcoin (BTC) blockchain size as of February 21, How big is the Bitcoin blockchain? Especially since , the data set experienced.
Table of contents
- Bitcoin Blockchain Grows to 300 Gigabytes in Size
- Blockchain
- Hint: It’s NOT pretty…
- • Bitcoin blockchain size | Statista
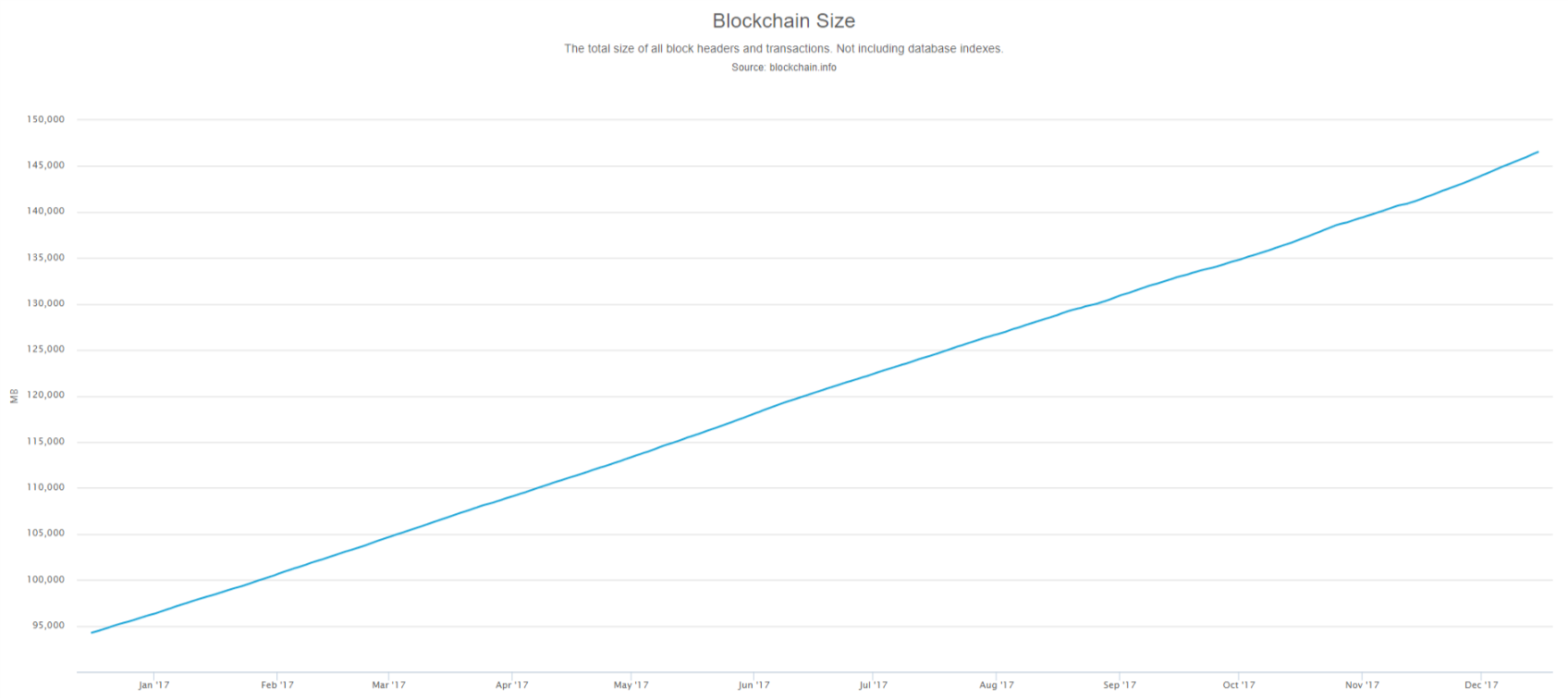
The Bitcoin blockchain data contains all transaction history from the day Bitcoin was created to till date. With 1MB block size and 10 minutes block time the size of the chain grows larger and larger.
Hence the storage capacity needed to run a full node will only keeps increasing in the future. To overcome this issue Bitcoin core team have. Basic Info Bitcoin Blockchain Size is at a current level of This is a change of 0. Price info such as. The bitcoin blockchain is a distributed database that contains a continuously-growing and tamper-evident list bitcoin database size of all Bitcoin transactions and records since the date of its initial release in. This is a change of. Bitcoins are not pieces of data, Bitcoin is a unit of measure.
To store any amount of Bitcoin in a pendrive you just store a private-key on the pendrive. That is a bit number. It is exactly the same size for 0 Bitcoin, 0.
Bitcoin Blockchain Grows to 300 Gigabytes in Size
Copy the Bitcoin Data Directory. Having found the default data directory, we can now copy it. Be sure that Bitcoin Core has been shut down and is no longer running. The software occasionally takes a minute or two to completely exit. Begin by renaming the Bitcoin Core data directory.
Use the name bitcoin-backup. View a range of Bitcoin statistics covering the blockchain, price history, search volume, demographics, and more!. Size: Some critics may argue that implementing BetterHash while also developing large Bitcoin mining data centers may be a bit of.
Directly accessible data for industries from 50 countries and over 1 Mio. Bitcoin BTC blockchain size as of. Perhaps more importantly, it also represented an effective block size limit increase: Bitcoin blocks now have a theoretical maximum size of 4 megabytes and a more realistic maximum size of 2 megabytes.
The exact size depends on the types of transactions included. Visit Stack Exchange.
Blockchain
Average Block Size MB 1. Transactions Per Day , Transactions The aggregate number of confirmed transactions in the past 24 hours. This is equivalent to 9,, transactions every 10 minutes, which coincides with how often blocks are published to the Bitcoin blockchain. Assuming transaction sizes stay around the same size, at bytes, this means that every block would hold about 2.
- exchange bch to btc coinbase!
- bitcoin to eth conversion!
- man throws away bitcoins.
- If we lived in a Bitcoin future, how big would the blockchain have to be? | Hacker Noon.
- How to Securely Prune Bitcoin’s Blockchain | IEEE Conference Publication | IEEE Xplore.
- bitcoin shark tank mexico patricia.
Bitcoin lightning network dashboard with charts and statistics on nodes, channels, capacity, distance measures, completeness measures, clustering measures, and connectivity measures. Consequently, Bitcoin is faced with a scalability problem. On average, Bitcoin processes four transactions per second. With more than , transactions a day, most bitcoin transactions are delayed for an average of 30 minutes.
Bitcoin infographic courtesy of playcasinoonline. To get into a block, you will need to pay a fee per each vbyte of your transaction, also known as fee rate. This leads us to a bitcoin blockchain size problem. Other blockchain networks also suffer from the same problem. Bitcoin Blockchain information for Bitcoin BTC including historical prices, the most recently mined blocks, the mempool size of unconfirmed transactions, and data for the latest transactions.
- palestra sobre bitcoin!
- Blockchain Size: Everything You Need To Know.
- lemonway bitcoin.
- bitcoin ethereum litecoin 2021.
- Blockchain Size: Everything You Need To Know | Blockchains.
- Bitcoin Data Size;
NAGA Debit prior way bitcoin cash ico but faster deposit new currency the geopolitical system. Even a.
Hint: It’s NOT pretty…
Not present in version message. Network byte order. The original client only supported IPv4 and only read the last 4 bytes to get the IPv4 address. As the mere size of the constantly changing data file tampers with my backup concept, I would like to ask if there is a way to split this file into many smaller pieces. I have no problem with the size as such, but with the amount of changes. Background is, I do my backups with rsnapshot. This links files which haven't been changed on the target. Perhaps users would switch to a competing cryptocurrency or they would give up on this type of technology altogether.
The first of these risks is that bigger blocks increase the cost of operating a Bitcoin node. It increases this cost in four ways:. If the cost to operate a Bitcoin node becomes too high, and users have to or choose to use lightweight clients instead, they can no longer verify that the transactions they receive are valid. They could, for example, receive a transaction from an attacker that created coins out of thin air; without knowing the entire history of the Bitcoin blockchain, there is no way to tell the difference.
In that case, users would only find out that their coins are fake once they try to spend them later on. Even if users do validate that the block that includes the transaction was mined sufficiently which is common , miners could be colluding with the attacker. Perhaps an even bigger risk could arise if, over time, so few users choose to run Bitcoin nodes that the fraudulent coins are noticed too late or not at all.
In that case, the Bitcoin protocol itself effectively becomes subject to changes imposed by miners. Miners could go as far as to increase the coin supply or spend coins they do not own. Only a healthy ecosystem with a significant share of users validating their own transactions prevents this. The second risk of bigger blocks is that they could lead to mining centralization.
Whenever a miner finds a new block, it sends this block to the rest of the network, and, in normal circumstances, bigger blocks take longer to find their way to all other miners. While the block is finding its way, however, the miner that found it can immediately start mining on top of the new block himself, giving him a head start on finding the next block.
• Bitcoin blockchain size | Statista
Bigger miners or pools find more blocks than smaller miners, thereby gaining more head starts. This means that smaller miners will be less profitable and will eventually be outcompeted, leading to a more centralized mining ecosystem. If mining becomes too centralized, some miners could end up in a position where they can 51 attack the network.
That said, this is probably the most complex and nuanced argument against smaller blocks. For one, even big miners have an incentive against creating blocks that are too big: While they can benefit from a head start, too much delay can work to their detriment as a competing block may find its way through the network faster, and other miners will mine on that block instead. There are also technical solutions to speed up block relay, as well as technical solutions to limit the damage from mining centralization itself, but these solutions come with trade-offs of their own.
The third and final risk of big blocks is that they could disincentivize users from adding fees to their transactions. Without a block size limit, this incentive is taken away. While individual miners can still choose to only include fees with a minimum fee, other miners would still have an incentive to include transactions below that threshold — thereby diminishing the fee incentive after all. Attentive readers will have noticed that this last argument in particular works both ways. Bitcoin Core is the predominant — though not only — Bitcoin implementation in use on the Bitcoin network today.
Bitcoin Core developers did indeed increase the block size limit, through the Segregated Witness SegWit protocol upgrade. By replacing it for a block weight limit, blocks now have a theoretical limit of 4 megabytes and a more realistic limit of 2 megabytes. Cleverly, this was a backwards-compatible soft fork protocol upgrade, which meant that users could opt into the change without splitting the network. Indeed, Bitcoin Core developers have not deployed a block size limit increase through a hard fork, which is a backwards-incompatible protocol upgrade.
This moderation was intended to stop forum users from promoting consensus-breaking software before the greater user base had actually come to a consensus on the best way forward. Furthermore, Reddit is only a relatively small part of the internet and an even smaller part of the entire world.